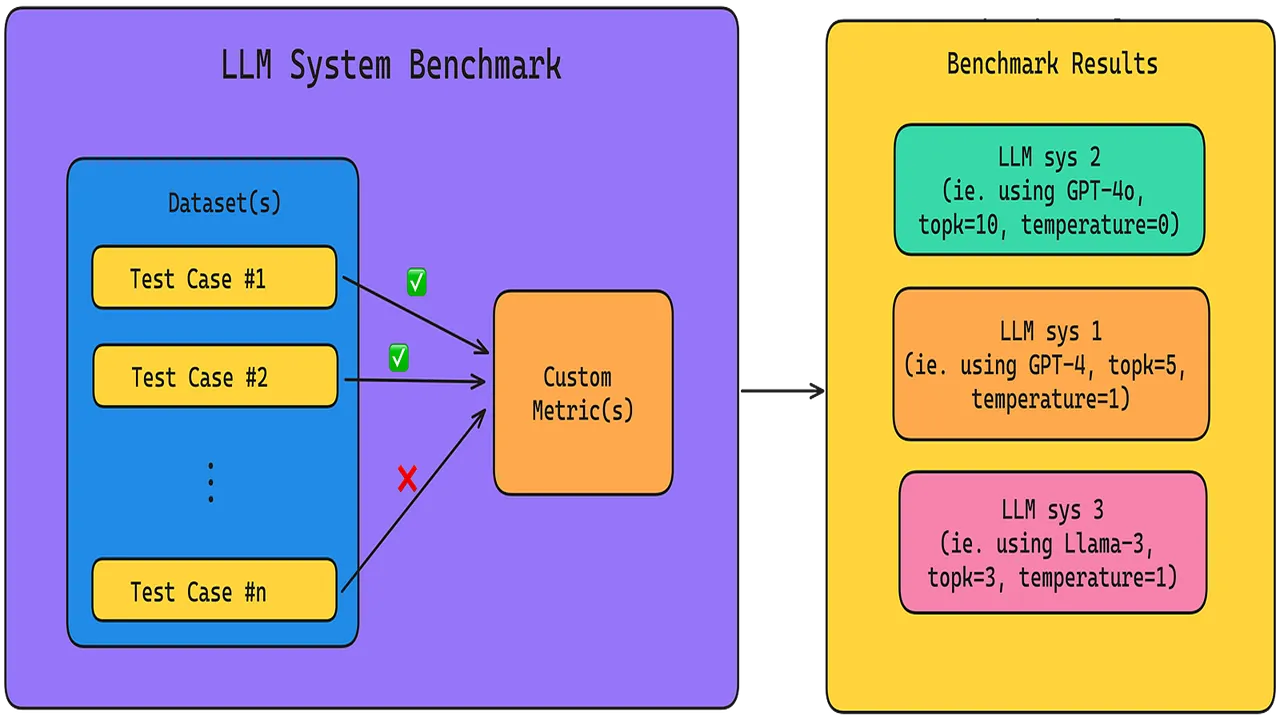
In May 2025, the open-source AI developer community introduced several new important tools (benchmarks) aimed at the standardized assessment of the safety and robustness of large language models (LLMs). Among the key developments is Phare, created by Giskard in collaboration with Google DeepMind. Phare allows LLMs to be evaluated on critical parameters such as their propensity for hallucinations, factual accuracy of responses, presence of bias, and potential harm from content; the benchmark supports English, French, and Spanish and provides open metrics for assessing the reliability of generative AI in real-world applications. Another significant tool is Agent-SafetyBench, a suite of 349 interactive environments and 2,000 tests covering 8 risk categories and 2,000 types of LLM agent failures. An initial assessment of 16 popular LLM agents using Agent-SafetyBench showed that none achieved a safety level above 60%, highlighting an urgent need for improvements. Additionally, the AgentHarm benchmark was introduced, focusing on assessing the maliciousness of LLM agents through 110 tasks simulating overtly harmful behavior. Its evaluation revealed that modern LLM agents can perform malicious actions even without complex circumvention of built-in safeguards. These new tools play a key role in increasing transparency and fostering the development of safer and more reliable AI systems.
New Open-Source Benchmarks for LLM Safety and Robustness Unveiled in May 2025